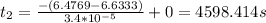Answer:
4600s
Step-by-step explanation:
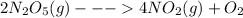
For a first order reaction the rate of reaction just depends on the concentration of one specie [B] and it’s expressed as:
![-(d[B])/(dt)=k[B] - - - -(d[B])/([B])=k*dt](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/54qm6jery2x1v12be8ln2c85u9iu1wsdrz.png)
If we have an ideal gas in an isothermal (T=constant) and isocoric (v=constant) process.
PV=nRT we can say that P = n so we can express the reaction order as a function of the Partial pressure of one component.
![-(d[P(B)])/(P(B))=k*dt](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/94mkz304ob3cbl7zjmm2qm38y9lzssoh2t.png)
![-(d[P(N_(2)O_(5))])/(P(N_(2)O_(5)))=k*dt](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/8kmsdbqv2empvdb42m9rlddc1mm3f4fm45.png)
Integrating we get:
![\int\limits^p \,-(d[P(N_(2)O_(5))])/(P(N_(2)O_(5)))=\int\limits^ t k*dt](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/oaavzo3gus1edhz85z3kwqo938e5nskw2i.png)
![-(ln[P(N_(2)O_(5))]-ln[P(N_(2)O_(5))_(o))])=k(t_(2)-t_(1))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/h42n7l508xkv4rqm2pfwn1gn3vnm1nuh61.png)
Clearing for t2:
![(-(ln[P(N_(2)O_(5))]-ln[P(N_(2)O_(5))_(o))]))/(k)+t_(1)=t_(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/mhxlg2b8bizdotyj35ipy07zzstap4cjnh.png)
![ln[P(N_(2)O_(5))]=ln(650)=6.4769](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/gqpghrrtc52qwl1bcoocres4foo0se6oaw.png)
![ln[P(N_(2)O_(5))_(o)]=ln(760)=6.6333](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/oc4iniua9isbn5rtmq3exi0t5s36avlk3x.png)