We are given the expression:
![\int\limits {\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{x} }*\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{ 1-x^(2)}} } \, dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/6md10w2xk3fdpm64bwixu9euaunvzs0ij4.png)
U-substitution:
let u =
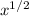 [So, x = u²]
[So, x = u²]
![(du)/(dx) = \frac{1}{2\sqrt[]{x}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/p74zqhjzgy0i3k3ygk7qcj9r90cedv0tfp.png) [differentiating both sides wrt x]
[differentiating both sides wrt x]
dx = du*2√(x)
dx = 2u(du) [Since u = √x]
Finding the Integral:
Plugging these values in the given expression:
![\int\limits {u^(-1)*(1-u^(2))^(-1/2) } \, 2\sqrt[]{x}*du](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/7b76166s2kgs3ib17xf05ng6jd43lctuig.png)
![\int\limits {(1)/(u)*\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{ 1-u^(2)}}*2u } \, du](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/o0twpjzyhb49ax2fvrkhh7kyub1gelfxpo.png)
The 'u' in the numerator and denominator will cancel out
![\int\limits {\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{ 1-u^(2)}}*2 } \, du](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/81zruo7netxf7llz9wwuuuuxveaovh5xqc.png)
Since 2 is a constant
![2\int\limits {\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{ 1-u^(2)}} } \, du](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/weakddyjcje5vkweg4se4a9w4s69271pfu.png)
Using the property:
![\int\limits {\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{1-x^(2)} }} \, dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/y7sbh7a54x9pokw8swf1w95k3hz8zwosit.png) = ArcSin(x) + C
= ArcSin(x) + C
2*ArcSin(u) + C
Since u = √x :
2*ArcSin(√x) + C