Answer:
The heat flows into the gas during this two-step process is 120 cal.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Number of moles = 3
Heat capacity at constant volume = 4.9 cal/mol.K
Heat capacity at constant pressure = 6.9 cal/mol.K
Initial temperature = 300 K
Final temperature = 320 K
We need to calculate the heat flow in to gas at constant pressure
Using formula of heat
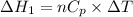
Put the value into the formula
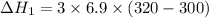
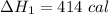
We need to calculate the heat flow in to gas at constant volume
Using formula of heat
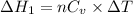
Put the value into the formula
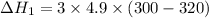
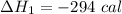
We need to calculate the heat flows into the gas during two steps
Using formula of total heat
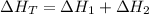
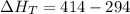
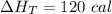
Hence, The heat flows into the gas during this two-step process is 120 cal.