Answer: Hello!
A second order differential equation has the next shape:
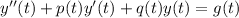
where p(t), q(t) and g(t) are functions of t, that can be constant numbers for example.
And is called homogeneus when g(t) = 0, so you have:
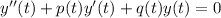
Then a second order differential equation is homogeneus ef every term involve either y or the derivatives of y.