Answer:
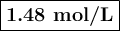
Step-by-step explanation:
We must use the Nernst equation
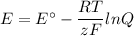
1. Calculate E°
Anode: Pd²⁺ (0.498 mol·L⁻¹) + 2e⁻ ⇌ Pd; E° = +0.987 V
Cathode: Cu ⇌ Cu⁺ (x mol·L⁻¹) + e⁻; E°= - 0.521 V
Overall: Pd²⁺(0.498 mol·L⁻¹) + 2Cu ⟶ Pd + 2Cu⁺ (x mol·L⁻¹); E° = 0.466 V
2. Calculate Q

3. Calculate [Cu⁺]
![\begin{array}{rcl}Q & = & \frac{\text{[Cu$^(+)$]}^(2)}{\text{[Pd]}}\\\\4.392 & = & \frac{{x}^(2)}{0.498}\\\\x^(2)& = & 2.187\\x & = & 1.48\\\end{array}\\\text{The concentration of Cu$^(+)$ is $\large \boxed{\textbf{1.48 mol/L}}$}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/qdj3ol6emaiif8fbynpqaoawgwl0sniw9m.png)