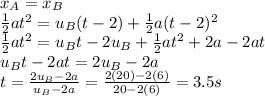Answer:
3. 3.5 s
Step-by-step explanation:
The position of traveller A is given by the equation:
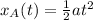
where
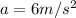 is the acceleration of A
is the acceleration of A
t is the time measured from when A started the motion
The position of traveller B instead is given by
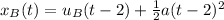
where a (acceleration) is the same as traveller A, and
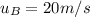
is B's initial velocity. We can verify that the formula is correct by substituting t=2, and we get
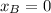 , which means that B starts its motion 2 seconds later.
, which means that B starts its motion 2 seconds later.
Traveller B overtakes traveller A when the two positions are the same, so: