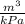Answer:
(a) V =
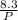
(b) (i) the value of
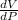 when P = 50kPa is - 0.00332
when P = 50kPa is - 0.00332
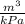
(ii) the meaning of the derivative
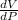 is the rate of change of volume with pressure.
is the rate of change of volume with pressure.
(iii) and the units are
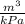
Step-by-step explanation:
Boyle's law states that at constant temperature;
P ∝ 1 / V
=> P = k / V
=> PV = k -------------------------(i)
Where;
P = pressure
V = volume
k = constant of proportionality
According to the question;
When;
V = 0.106m³, P = 50kPa
Substitute these values into equation (i) as follows;
50 x 0.106 = k
Solve for k;
k = 5.3 kPa m³
(a) To write V as a function of P, substitute the value of k into equation (i) as follows;
PV = k
PV = 8.3
Make V subject of the formula in the above equation as follows;
V = 8.3/P
=> V =
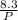 -------------------(ii)
-------------------(ii)
(b) Find the derivative of equation (ii) with respect to V to get dV/dP as follows;
V =
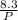
V = 8.3P⁻¹
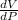 = -8.3P⁻²
= -8.3P⁻²
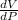 =
=
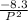
Now substitute P = 50kPa into the equation as follows;
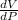 =
=
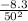 [
[
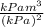 ] ----- Write and evaluate the units alongside
] ----- Write and evaluate the units alongside
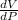 =
=
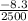 [
[
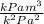 ]
]
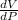 = - 0.00332 [
= - 0.00332 [
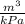 ]
]
Therefore,
(i) the value of
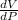 when P = 50kPa is - 0.00332
when P = 50kPa is - 0.00332
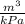
(ii) the meaning of the derivative
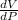 is the rate of change of volume with pressure.
is the rate of change of volume with pressure.
(iii) and the units are