Answer:
There is a 28.57% probability that a randomly selected participant who died by the end of the study was a non-smoker.
Explanation:
We have the following probabilities:
A 15% probability that a participant is classified as a heavy smoker.
A 25% probability that a participant is classified as a light smoker.
A 100% - 25% - 15% = 60% probability that a participant is classified as a non smoker.
A x% probability that a non smoker dies.
A 3x% probability that a light smoker dies.
A 5x% probability that a heavy smoker dies.
This can be formulated as the following problem:
What is the probability of B happening, knowing that A has happened.
It can be calculated by the following formula
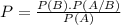
Where P(B) is the probability of B happening, P(A/B) is the probability of A happening knowing that B happened and P(A) is the probability of A happening.
This problem is:
What is the probability of the participant being a non-smoker, given that he died?
P(B) is the probability that the participant is a non smoker. So
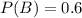
P(A/B) is the probability that the participant dies, given that he is a non smoker. So:
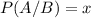
P(A) is the probability that the participant dies:
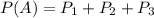
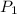 is the probability that a heavy smoker is selected and that he dies. So:
is the probability that a heavy smoker is selected and that he dies. So:
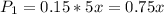
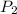 is the probability that a light smoker is selected and that he dies. So:
is the probability that a light smoker is selected and that he dies. So:
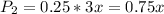
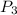 is the probability that a non-smoker is selected and that he dies. So:
is the probability that a non-smoker is selected and that he dies. So:
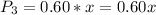
The probability that a participant dies is:
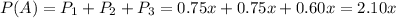
The probability of the participant being a non-smoker, given that he died, is:

There is a 28.57% probability that a randomly selected participant who died by the end of the study was a non-smoker.