Answer:
The concentration of PCl3 is 0.061 mol/L and for PCl5 is 0.002 mol/L
Step-by-step explanation:
The initial concentration of PCl5 is
n/V = 0.157/2.5 = 0.063 mol/L
During the reaction x mol/L is consumed, and x mol/L is formed of each product (the stoichiometry is 1 mol : 1 mol : 1 mol).
So, doing a table of reaction
PCl5 PCl3 Cl2
initial 0.063 0 0
reacted -x +x +x
equilibrium 0.063 - x x x
For a reaction aA + bB ↽−−⇀ cC +dD, the equilibrium constant is given by:
![Kc = ([C]^cx[D]^d)/([A]^ax[B]^b)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/aluwjelaqkxmyak3lxpjv5eji10y6280r7.png)
All these concentration are the concentration of equilibrium. So, for the reaction:
![Kc = ([PCl3]x[Cl2])/([PCl5])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ksizi9l9hdfonscbwwwicxadc08kxcl62h.png)
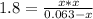
x² = 0.1134 - 1.8x
x² + 1.8x - 0.1134 = 0
Using Bhaskara, with a = 1, b = 1.8, and c = -0.1134
Δ = b² - 4ac = (1.8)² - 4*1*(-0.1134) = 3.6936
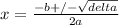
x is a molar concentration, so it must be positive, then:
x = (-1.8 + √3.6936)/2
x = 0.061 mol/L
Which is the concentration of PCl3. The concentration of PCl5 is
0.063 - 0.061 = 0.002 mol/L