Answer:
- P in PBr3 is +3.
- N in N2 is 0.
- As in H3AsO4 is +5.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, since the determination of the oxidation states is performed by using the well-known charge balances, we can proceed as shown below:
- P in PBr3: Here, bromide ions have an oxidation state of -1, so we follow:
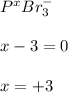
Thus, the oxidation state is +3.
- N in N2: Here, since nitrogen is bonding with nitrogen and it is neutral, we infer its oxidation state is 0.
- As in H3AsO4: Here, oxygen is -2 and hydrogen +1, so we follow:
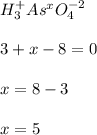
Thus, the oxidation state is +5.
Best regards!