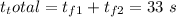Answer:
33 seconds.
Step-by-step explanation:
The equation for speed with constant acceleration at time t its:
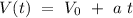
where
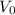 is the initial speed, and a its the acceleration.
is the initial speed, and a its the acceleration.
First half of the problem
Starting at rest, the initial speed will be zero, so
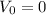
the final speed is
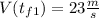
and the acceleration is
 .
.
Taking all this together, we got
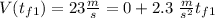
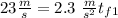
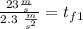
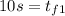
So, for the first half of the problem we got a time of 10 seconds.
Second half of the problem
Now, the initial speed will be
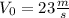 ,
,
the acceleration
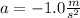 ,
,
with a minus sign cause its slowing down, the final speed will be
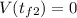
Taking all together:
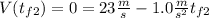
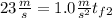
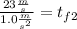
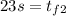
So, for the first half of the problem we got a time of 23 seconds.
Total time