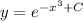Answer:
The general solution of the differential equation y' + 3x^2 y = 0 is:
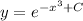
Explanation:
This equation its a Separable First Order Differential Equation, this means that you can express the equation in the following way:
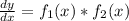 , notice that the notation for y' is changed to
, notice that the notation for y' is changed to
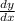
Then you can separate the equation and put the x part of the equation on one side and the y part on the other, like this:
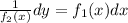
The Next step is to integrate both sides of the equation separately and then simplify the equation.
For the differential equation in question y' + 3x^2 y = 0 the process is:
Step 1: Separate the x part and the y part
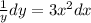
Step 2: Integrate both sides
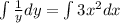
Step 3: Solve the integrals
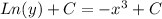
Simplify the equation:
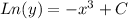
To solve the Logarithmic expression you have to use the exponential e
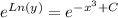
Then the solution is: