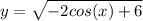Answer:
The solution for this differential equation is
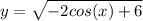
Explanation:
This differential equation
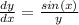 is a separable First-Order ordinary differential equation.
is a separable First-Order ordinary differential equation.
We know this because a first-order differential equation is separable if and only if it can be written as
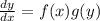 where f and g are known functions.
where f and g are known functions.
And we have
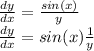
To solve this differential equation we need to integrate both sides
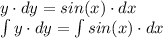
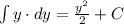
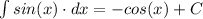
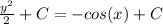
We can make a new constant of integration
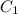
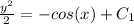
We need to isolate y
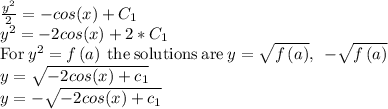
We have the initial conditions y(0)=2 so we can find the value of the constant of integration for
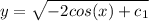
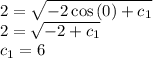
For
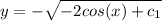 there is not solution for
there is not solution for
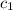 in the domain of real numbers.
in the domain of real numbers.
The solution for this differential equation is