Answer:
28.8 meters
Step-by-step explanation:
We must first determine at which velocity the ball hits the water. To do so we will:
1) Assume no air resistance.
2) Use the Law of conservation of mechanical energy: E=K+P
Where
E is the mechanical energy (which is constant)
K is the kinetic energy.
P is the potential energy.
With this we have
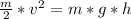
Where:
m is the balls's mass <- we will see that it cancels out and as such we don't need to know it.
v is the speed when it hits the water.
g is the gravitational constant (we will assume g=9.8
 .
.
h is the height from which the ball fell.
Because when we initially drop the ball, all its energy is potential (and
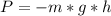 ) and when it hits the water, all its energy is kinetic (
) and when it hits the water, all its energy is kinetic (
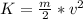 . And all that potential was converted to kinetic energy.
. And all that potential was converted to kinetic energy.
Now, from
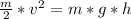 we can deduce that
we can deduce that
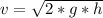
Therefore v=9.6
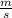
Now, to answer how deep is the lake we just need to multiply that speed by the time it took the ball to reach the bottom.
So D=9.6
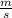 *3
*3
 =28.8
=28.8
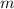
Which is our answer.