Answer:
The atmospheric pressure is
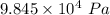
Step-by-step explanation:
There are two ways of solving this exercise:
1)
In physics you can find that mmHg is a unit of pressure.
Pressure = Force/area.
If you consider the weight of mercury as your force (mass* acceleration of gravity = density*volume* acceleration of gravity ), then
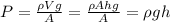
where h is the height of the mercury column and rho its density.
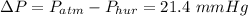 .
.
if normal atmospheric pressure is
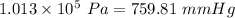
then the pressure in the presence of the hurricane is
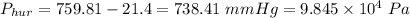
2)
Considering the definition of pressure
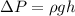
where
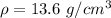 ,
,
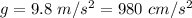 and
and
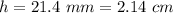 .
.
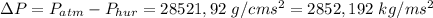 , where
, where
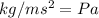 .
.
if
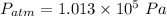 ,
,
then
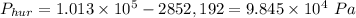 .
.