Answer:
0.004548 M is the concentration of B at equilibrium at 500 K.
Step-by-step explanation:
A(aq) ⇆ 2 B(aq)
Initially 3.00 M
At equilibrium 3.00 -x 2x
Equilibrium constant of the reaction at 500 K =
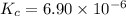
Concentration of A at 500 K at equilibrium , [A] = (3.00 -x )M
Concentration of B at 500 K at equilibrium,[B]= 2x
An expression of equilibrium constant is given as:
![K_c=([B]^2)/([A])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/wrys4m0sg1gf9z4lwx3n6zrxhpwznkx4kj.png)
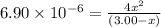
On solving for x:
x = 0.002274 M
[B] = 2 x = 2 × 0.002274 M = 0.004548 M
[A] = (3-x) = 3 M - 0.002274 M =2.997726 M
0.004548 M is the concentration of B at equilibrium.