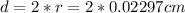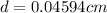Answer:
0.04594 cm
Step-by-step explanation:
So, we need the wire melt when the max current density its
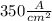 . Now, we got our limit current, 0.58 A.
. Now, we got our limit current, 0.58 A.
The current density its
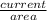 , so, with our data, we can obtain the cross area of the wire.
, so, with our data, we can obtain the cross area of the wire.
For a cylinder, the area its given by:
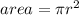
We can put all this in the equation for the max current density:
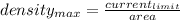
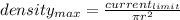
And now, we can work it a little:
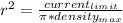
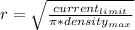
using our values, max current density =
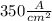 , and limit current = 0.58 A,
, and limit current = 0.58 A,
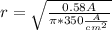
And, of course, the diameter its two times the radius: