Answer:
Explanation:
X no of questions student answers is binomial with n =40 and p =0.5
If approximated to normal, X is Normal with
mean = np = 20 and variance = npq = 10
P(X>N) >0.10
We use std normal distribution table to get z value first then convert to x value
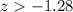
So
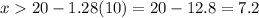
This is with continuity correction.
Hence without continuity correction this equals 7.2-0.5 = 6.7
x>6.7
n = 7