Answer: The net change in the atoms is the conversion of a neutron to a proton, turning Carbon (6 protons) into Nitrogen (7 protons).
Step-by-step explanation:
Carbon-14, generated from the atmosphere, has 6 protons and 8 neutrons. That's where the 14 comes from, called the mass number, is the sum of protons and neutrons (6+8=14).
Carbon-14 is radioactive and decays by beta decay. That means one of its neutrons spontaneously turns into a proton, an electron, and a neutrino, according to:
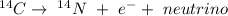
After that, the atom has 7 protons and 7 neutrons, maintaining its mass number but changing its atomic number from 6 to 7, turning into Nitrogen.