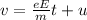Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that, the electron is moving parallel to the electric field.
Then the electron experience a force which is given by,
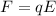
Therefore,
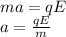
And q=e, and the acceleration is defines as,
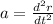
Here, r is the the path traced by an electron.
Now equate the acceleration.
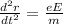
Now integrate both side with respect to t.
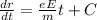
Now, consider at t=0 the initial velocity of electron is u.
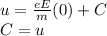
Therefore the velocity of an electron is,