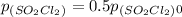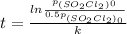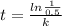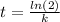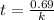Answer: The time is 0.69/k seconds
Step-by-step explanation:
The following integrated first order rate law
ln[SO₂Cl₂] - ln[SO₂Cl₂]₀ = - k×t
where
[SO₂Cl₂] concentration at time t,
[SO₂Cl₂]₀ initial concentration,
k rate constant
Therefore, the time elapsed after a certain concentration variation is given by:
![t=(ln[SO_(2)Cl_(2)]_(0) - ln[SO_(2)Cl_(2)])/(k)=(ln([SO_(2)Cl_(2)]_(0))/([SO_(2)Cl_(2)]) )/(k)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/kklzhkur1g48r6iigab6qsismt51cemn2j.png)
We could assume that SO₂Cl₂ behaves as a ideal gas mixture so partial pressure is proportional to concentration:
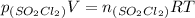
![[SO_(2)Cl_(2)]= \frac{n_{(SO_(2)Cl_(2))}}{V}}=\frac{p_{(SO_(2)Cl_(2))}}{RT}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/8r29wqmwkxrrnc3hu9z4esmf30arf9p3v1.png)
In conclusion,
t = ln( p(SO₂Cl₂)₀/p(SO₂Cl₂) )/k
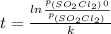
for