Answer : The correct option is, (b) +0.799 V
Solution :
The values of standard reduction electrode potential of the cell are:
![E^0_([H^(+)/H_2])=+0.00V](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ijcqo69elt8hof70g4qi2r4obrqkikin90.png)
![E^0_([Ag^(+)/Ag])=+0.799V](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/y7kk19iimw1oz10gopyvyl17lqjpalb1t8.png)
From the cell representation we conclude that, the hydrogen (H) undergoes oxidation by loss of electrons and thus act as anode. Silver (Ag) undergoes reduction by gain of electrons and thus act as cathode.
The half reaction will be:
Reaction at anode (oxidation) :
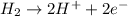
Reaction at cathode (reduction) :
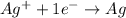
The balanced cell reaction will be,
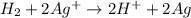
Now we have to calculate the standard electrode potential of the cell.
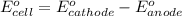
![E^o_(cell)=E^o_([Ag^(+)/Ag])-E^o_([H^(+)/H_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/nszs9iz70aw940bxn8fjjvc18ouizi2aij.png)
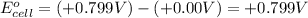
Therefore, the standard cell potential will be +0.799 V