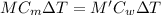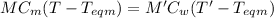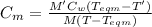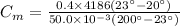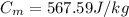Answer:
Specific heat of metal,
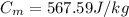
Given:
Mass of metal, M = 50.0 g = 0.05 kg
Initial temperature, T =
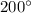
Mass of water, M' = 400 g = 0.4 kg
Temperature for water, T' =
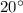
Equilibrium temperature,
![T_(eqm) = [tex]23^(\circ)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/3kodyyempkg001i1l13vl9n47rhjffbss7.png)
specific heat of water,
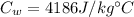
Solution:
At equilibrium:
specific heat of metal = specific heat of water
Therefore,