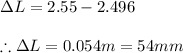Answer:
The length contracts by 54 mm.
Step-by-step explanation:
According to theory of special relativity the contraction in the length of an object travelling at a speed 'v' is given by
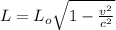
where
L = contracted length of the object
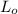 = original length of object
= original length of object
v = speed of the object
c = speed of light
Applying values we get
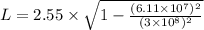
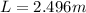
Thus the change in length equals