Step-by-step explanation:
It is known that
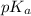 value of acetic acid is 4.74. And, relation between pH and
value of acetic acid is 4.74. And, relation between pH and
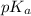 is as follows.
is as follows.
pH = pK_{a} + log
![([CH_(3)COOH])/([CH_(3)COONa])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/8nww7g443rfdces8zgj7qv4hp0aw12loho.png)
= 4.74 + log
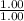
So, number of moles of NaOH = Volume × Molarity
= 71.0 ml × 0.760 M
= 0.05396 mol
Also, moles of
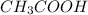 = moles of
= moles of
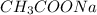
= Molarity × Volume
= 1.00 M × 1.00 L
= 1.00 mol
Hence, addition of sodium acetate in NaOH will lead to the formation of acetic acid as follows.
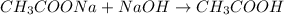
Initial : 1.00 mol 1.00 mol
NaoH addition: 0.05396 mol
Equilibrium : (1 - 0.05396 mol) 0 (1.00 + 0.05396 mol)
= 0.94604 mol = 1.05396 mol
As, pH = pK_{a} + log
![([CH_(3)COONa])/([CH_(3)COOH])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ae75gygawijsgwrkadxxrz4qj82jeivfzt.png)
= 4.74 + log
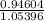
= 4.69
Therefore, change in pH will be calculated as follows.
pH = 4.74 - 4.69
= 0.05
Thus, we can conclude that change in pH of the given solution is 0.05.