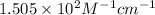Answer : The molar absorptivity coefficient is,
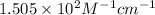
Explanation :
Using Beer-Lambert's law :
Formula used :

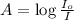
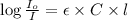
where,
A = absorbance of solution
C = concentration of solution =
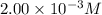
l = path length = 1.00 cm
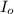 = incident light
= incident light
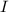 = transmitted light
= transmitted light
 = molar absorptivity coefficient = ?
= molar absorptivity coefficient = ?
A compound absorb 50 % of the light that means,
Incident light =
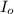
Transmitted light =
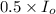
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get the molar absorptivity coefficient.
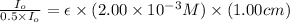
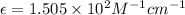
Therefore, the molar absorptivity coefficient is,