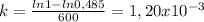Answer:
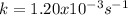
Step-by-step explanation:
For a first order reaction the rate law is:
![v=(-d[A])/([A])=k[A]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/rm2bjn8iqrjqpvu1trfcl4xlhi21o9etq8.png)
Integranting both sides of the equation we get:
![\int\limits^a_b {(d[A])/([A])} \, dx =-k\int\limits^t_0 {} \, dt](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/2qhpgerbzuvp0ksvwwdn9ufmj5bognv9qc.png)
where "a" stands for [A] (molar concentration of a given reagent) and "b" is {A]0 (initial molar concentration of a given reagent), "t" is the time in seconds.
From that integral we get the integrated rate law:
![ln([A])/([A]_(0) ) =-kt](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/r9k73u3l6nr1h0w4vvbcyhs5n8bk3bx4n3.png)
![[A]=[A]_(0)e^(-kt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/llgveeixbn498q40gq28x54eufc4o9etim.png)
![ln[A]=ln[A]_(0) -kt](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ig8ke3ae18j221ppacp3j6apy6ze7v1bh8.png)
![k=(ln[A]_(0)-ln[A])/(t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/8cpr0qukrmm6z84zgxel7hd71o7cnw07sr.png)
therefore k is