Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
E.m.f = 12 V, Voltage = 10 V, Resistance = 2 ohm
Hence, calculate the current as follows.
I =
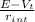
Putting the given values into the above formula as follows.
I =
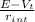
=
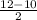
= 1 A
Atomic weight of copper is 63.54 g/mol. Therefore, equivalent weight of copper is
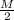 .
.
That is,
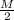
=
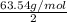
Hence, electrochemical equivalent of copper is as follows.
Z = (\frac{E}{96500}) g/C
= (\frac{63.54 g/mol}{2 \times 96500}) g/C
=
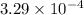 g/C
g/C
Therefore, charge delivered from the battery in half-hour is calculated as follows.
It = Q
=
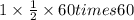
= 1800 C
So, copper deposited at the cathode in half-an-hour is as follows.
M = ZQ
=
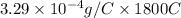
= 0.5927 g
Thus, we can conclude that 0.5927 g of copper is deposited at the cathode in half an hour.