Answer:
The general solution of given differential equation is
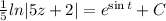 .
.
Explanation:
The given differential equation is
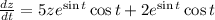
Taking out common factors.
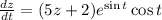
Using variable separable method, we get
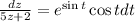
Integrate both sides.
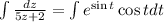
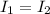 .... (1)
.... (1)
First solve LHS,
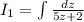
Substitute
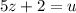
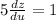
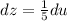
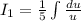
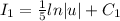
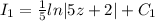
Now, solve RHS,
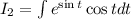
Substitute
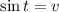 ,
,
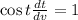
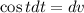
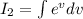
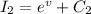
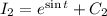
Subtitle the values of I₁ and I₂ in equation (1).
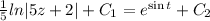
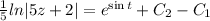
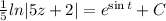
Therefore the general solution of given differential equation is
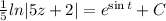 .
.