Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
Mass of the hockey puck, m = 300 g = 0.3 kg
Initial speed of the puck, u = 40 m/s
Finally, it comes to rest, v = 0
Distance covered, s = 30 m
(a) We need to find the energy of the puck changes over time. It can be calculated using the work energy theorem as :
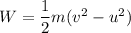
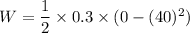
W = -240 J
(b) The net friction force can be calculated using the definition of work done.
Since,
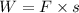
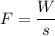
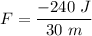
F = -8 N
The minus sign shows the friction force as it acts in the opposite direction of motion. Hence, this is the required solution.