Explanation :
The standard reduction potentials for zinc and copper are:
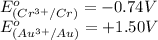
The substance having highest positive
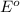 potential will always get reduced and will undergo reduction reaction.
potential will always get reduced and will undergo reduction reaction.
Here, gold will undergo reduction reaction will get reduced. Chromium will undergo oxidation reaction and will get oxidized.
(a) The oxidation-reduction half cell reaction will be,
Oxidation half reaction:
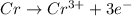
Reduction half reaction:
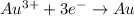
(b) Oxidation reaction occurs at anode and reduction reaction occurs at cathode. That means, gold shows reduction and occurs at cathode and chromium shows oxidation and occurs at anode.
(c) The overall balanced equation of the cell is,
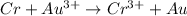
(d) To calculate the
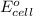 of the reaction, we use the equation:
of the reaction, we use the equation:
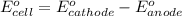
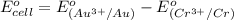
Putting values in above equation, we get:
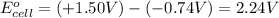
Hence, the standard potential for the given cell is 2.24 V