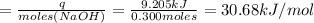Answer:
ΔH(neu) = 30.68 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction between HCl (strong acid) and NaOH(strong base) is a neutralization reaction which yields sodium chloride NaCl and water
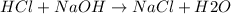
The heat (q) of a reaction is given as:
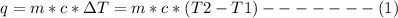
where m = mass of the system
c = specific heat
T1 and T2 are the initial and final temperatures
It is given that:
Volume of HCl = 1000 ml
Volume of NaOH = 100.0 ml
Density of HCl and NaOH = 1.000 g/ml
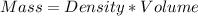
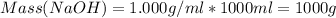
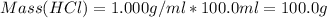
Total mass of the solutions, m = 1000 +100.0 = 1100.0 g
c = 4.184 J/g/c
T1 = 20.0C
T2 = 22.0 C
Substituting appropriate values in equation (1) gives:

Now, the number of moles of NaOH is:
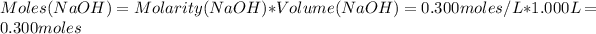
Enthalpy of neutralization is: