Step-by-step explanation:
The given reaction is as follows.
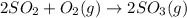
Value of equilibrium constant is given as
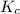 = 4.3 \times 10^{6}[/tex].
= 4.3 \times 10^{6}[/tex].
Concentration of given species is
![[SO_2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/iragxlotv7fynhtzk51bo047gouj0vdgvk.png) = 0.010 M;
= 0.010 M;
![[SO_3]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/cf56dwobaje5ymnwzisu2eafq5mi45yoj9.png) = 10.M;
= 10.M;
![[O_2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ngke6m6k9deep00fr55hbg5jnvxrxzrnj0.png) = 0.010 M.
= 0.010 M.
Formula for experimental value of equilibrium constant (Q) is as follows.
Q =
![([SO_(3)]^(2))/([SO_(2)]^(2)[O_(2)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/h64f8bg24d4s6nrecvhugazdbzpci6ifxz.png)
Putting the given concentration as follows.
Q =
![([SO_(3)]^(2))/([SO_(2)]^(2)[O_(2)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/h64f8bg24d4s6nrecvhugazdbzpci6ifxz.png)
Q =
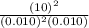
Q =
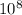
It is known that when Q >
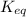 , then reaction moves in the backward direction.
, then reaction moves in the backward direction.
When Q <
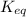 , then reaction moves in the forward direction.
, then reaction moves in the forward direction.
When Q =
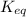 , then reaction is at equilibrium.
, then reaction is at equilibrium.
As, for the given reaction Q >
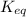 then it means reaction moves in the backward direction.
then it means reaction moves in the backward direction.
Thus, we can conclude that the reaction is moving in the backward direction, that is, right to left to reach the equilibrium.