Answer:
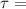 2452.5 N/m^2
2452.5 N/m^2
Step-by-step explanation:
given:
density
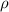 =500kg/m^3
=500kg/m^3
viscosity
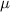 = 10 Pa-s
= 10 Pa-s
diameter of tube= 2 m
and L be length
since gravity is the only force shear force will balance it
so we can write
mg=

A=
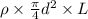
m=
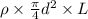
therefore
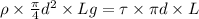
putting values we get
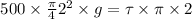
calculating we get
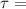 2452.5 N/m^2
2452.5 N/m^2