Step-by-step explanation:
The given reaction is as follows.
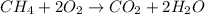
As it is known that number of moles equal mass divided by molar mass. Molar mass of methane is 16 g/mol.
Hence, No. of moles =
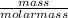
=
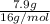
= 0.493 mol
Molar mass of oxygen is 32 g/mol.
Hence, its number of moles =
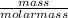
=
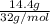
= 0.45 mol
As, it is shown from the reaction that 1 mole of methane needs 2 mole of oxygen.
Therefore, 0.493 mol of methane needs
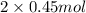 equals 0.9 moles of oxygen.
equals 0.9 moles of oxygen.
As there is only 0.45 moles of oxygen for the reaction. So, it means that oxygen is the limiting reagent.
Hence, for 0.45 moles of oxygen, methane required is as follows.
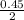 = 0.225 moles
= 0.225 moles
So, 0.225 moles of methane is equal to
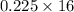 = 3.6 g
= 3.6 g
As, 3.6 g of methane reacts with oxygen. Therefore, amount of methane remains is calculated as follows.
(7.9 g - 3.6 g) = 4.3 g
Thus, we can conclude that the minimum mass of methane that could be left over by the chemical reaction is 4.3 g.