Answer:
(A) The carboxylate carbon
Step-by-step explanation:
Pyruvate is produced as a product of glycolysis in cytoplasm.
Pyruvate oxidation takes place in mitochondrial matrix. Here, these steps are followed:
Step 1. The carboxyl group of the pyruvate is snipped off and is released as a carbon dioxide.
Step 2. The molecule containing 2 carbons produced from the step 1 is oxidized, and the electrons lost in the oxidation are picked up by
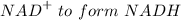
Step 3. The oxidized two-carbon molecule gets attached to Coenzyme A and forms acetyl CoA.