Answer:
2nd choice.
Explanation:
Let's compare the following:
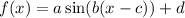 to
to
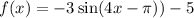 .
.
They are almost in the same form.
The amplitude is |a|, so it isn't going to be negative.
The period is
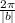 .
.
The phase shift is
 .
.
If c is positive it has been shifted right c units.
If c is negative it has been shifted left c units.
d is the vertical shift.
If d is negative, it has been moved down d units.
If d is positive, it has been moved up d units.
So we already know two things:
The amplitude is |a|=|-3|=3.
The vertical shift is d=-5 which means it was moved down 5 units from the parent function.
Now let's find the others.
I'm going to factor out 4 from
 .
.
Like this:
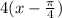
Now if you compare this to
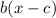
then b=4 so the period is
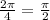 .
.
Also in place of c you see
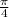 which means the phase shift is
which means the phase shift is
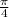 .
.
The second choice is what we are looking for.