Answer:
When the net external force is zero
Step-by-step explanation:
We can answer to this question by referring to Newton's Second Law, which can be written in the following form
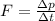
where
F is the net external force acting on a system
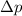 is the change in momentum of the system
is the change in momentum of the system
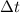 is the time interval
is the time interval
When the total momentum of a system is conserved (so, it does not change), its variation is zero:
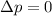
In order to satisfy this condition, we see from the formula that we must also have
F = 0
so the net external force acting on the system must be zero.