Answer:
a).f =68.75 cm
b). focal length will be 100 times larger.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given :
Refractive index of the lens, n = 1.6
Front surface radius,
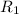 = 11 cm
= 11 cm
Back surface radius,
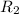 = 15 cm
= 15 cm
Therefore we know for a focal length that
a). Focal length,
![(1)/(f) = (n-1)\left [ (1)/(R_(1)) -(1)/(R_(2))\right ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/yzuj6s3w93xozjpf8oaqoj7idkrlnj4g01.png)
![(1)/(f) = (1.6-1)\left [ (1)/(11) -(1)/(15)\right ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/fau1zlvxhr2ran6ycyirx3l5obclh4lqnj.png)
![(1)/(f) = (0.6)* \left [ (15-11)/(15* 11) \right ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/9nowdi2p4b1yd6lnpw31b5bnm0e2spxh1e.png)
f =68.75 cm
b). We know that aperture and focal length of lens are related directly. If aperture is small, focal length is small and when aperture is large , the focal length is more.
Thus, when the aperture is 100 times larger, the focal length will also be 100 times larger.