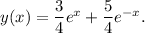Answer: The required solution of the given IVP is
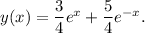
Step-by-step explanation: We are given to find the solution of the following initial value problem :
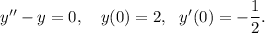
Let
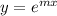 be an auxiliary solution of the given differential equation.
be an auxiliary solution of the given differential equation.
Then, we have

Substituting these values in the given differential equation, we have
![m^2e^(mx)-e^(mx)=0\\\\\Rightarrow (m^2-1)e^(mx)=0\\\\\Rightarrow m^2-1=0~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~[\textup{since }e^(mx)\\eq0]\\\\\Rightarrow m^2=1\\\\\Rightarrow m=\pm1.](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/d755uhyz0pky7y21keuh98l5v65seo8uc2.png)
So, the general solution of the given equation is
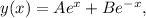 where A and B are constants.
where A and B are constants.
This gives, after differentiating with respect to x that
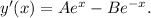
The given conditions implies that

and
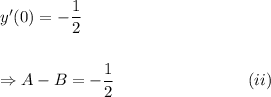
Adding equations (i) and (ii), we get
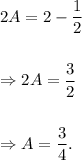
From equation (i), we get
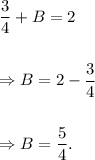
Substituting the values of A and B in the general solution, we get
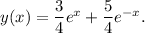
Thus, the required solution of the given IVP is