Answer: 80J
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the first principle of thermodynamics:
"Energy is not created, nor destroyed, but it is conserved."
Then this priciple (also called Law) relates the work and the transferred heat exchanged in a system through the internal energy
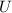 , which is neither created nor destroyed, it is only transformed. So, in this especific case of the compressed gas:
, which is neither created nor destroyed, it is only transformed. So, in this especific case of the compressed gas:
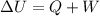 (1)
(1)
Where:
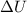 is the variation in the internal (thermal) energy of the system (the value we want to find)
is the variation in the internal (thermal) energy of the system (the value we want to find)
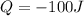 is the heat transferred out of the gas (that is why it is negative)
is the heat transferred out of the gas (that is why it is negative)
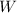 is the work is done on the gas (as the gas is compressed, the work done on the gas must be considered positive )
is the work is done on the gas (as the gas is compressed, the work done on the gas must be considered positive )
On the other hand, the work done on the gas is given by:
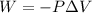 (2)
(2)
Where:
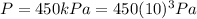 is the constant pressure of the gas
is the constant pressure of the gas
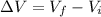 is the variation in volume of the gas
is the variation in volume of the gas
In this case the initial volume is
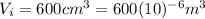 and the final volume is
and the final volume is
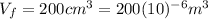 .
.
This means:
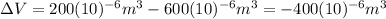 (3)
(3)
Substituting (3) in (2):
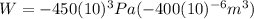 (4)
(4)
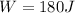 (5)
(5)
Substituting (5) in (1):
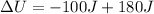 (6)
(6)
Finally:
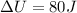 This is the change in thermal energy in the compression process.
This is the change in thermal energy in the compression process.