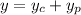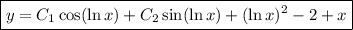For the corresponding homogeneous equation,
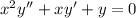
we can look for a solution of the form
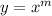 , with derivatives
, with derivatives
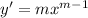 and
and
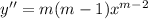 . Substituting these into the ODE gives
. Substituting these into the ODE gives
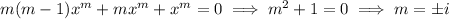
which admits two solutions,
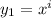 and
and
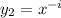 , which we can write as
, which we can write as
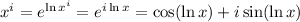
and by the same token,
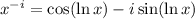
so we see two independent solutions that make up the characteristic solution,
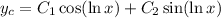
For the non-homogeneous ODE, we make the substitution
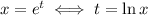
so that by the chain rule, the first derivative becomes
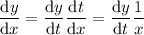
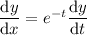
Let
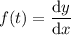 . Then the second derivative becomes
. Then the second derivative becomes
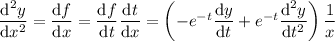
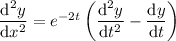
Substituting these into the ODE gives
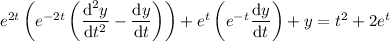
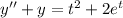
Look for a particular solution
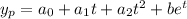 , which has second derivative
, which has second derivative
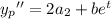 . Substituting these into the ODE gives
. Substituting these into the ODE gives
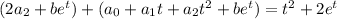
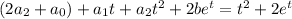
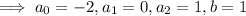
so that the particular solution is
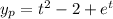
Solving in terms of
 gives the solution
gives the solution
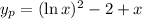
and the overall general solution is