A second order linear, non - homogeneous ODE has a form of
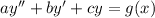
The general solution to,
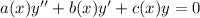
Can be written as,
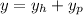
Where
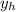 is a solution to the homogeneous ODE and
is a solution to the homogeneous ODE and
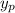 the particular solution, function that satisfies the non - homogeneous equation.
the particular solution, function that satisfies the non - homogeneous equation.
We can solve
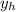 by rewriting the equation,
by rewriting the equation,
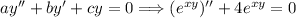
Which simplifies to,
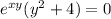
From here we get two solutions,
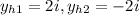
So the form here refines,
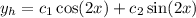
The same thing we do with
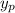 to get form of,
to get form of,
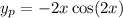
From here the final form emerges,
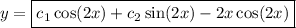
Hope this helps.
r3t40