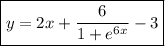Substitute
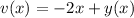 , so that
, so that
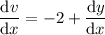 . Then the ODE is equivalent to
. Then the ODE is equivalent to
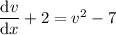
which is separable as
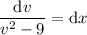
Split the left side into partial fractions,
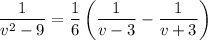
so that integrating both sides is trivial and we get
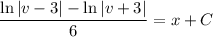
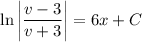
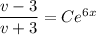
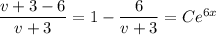
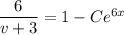
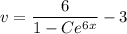
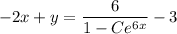
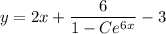
Given the initial condition
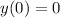 , we find
, we find
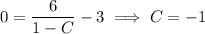
so that the ODE has the particular solution,