Answer:
Mole fraction of glycerol is 0.02666.
Volume of the mixture is 99.75 mL.
Step-by-step explanation:
Volume of glycerol,V = 10 mL
Mass of glycerol = m
Density of glycerol =
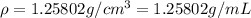
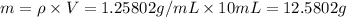
Volume of water,V' = 90 mL
Mass of water= m'
Density of water =
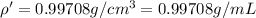
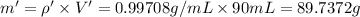
Mole fraction of glycerol =
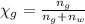
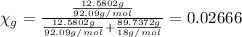
Volume of the solution: v
Mass of the solution = M = 12.5802 g + 89.7372 g =102.3174 g[/tex]
Density of the mixture =
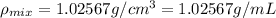
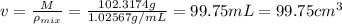
Volume of the mixture is 99.75 mL.
Theoretically the volume of the solution should be 100 ml.But experimentally the volume of the solution is 99.75 ml which is less than the theoretical volume.
This is because water molecules and glycerol molecules are getting associated with each other due to hydrogen bonding which results in less volume of the mixture.