Answer:
2C₆H₁₄ + 19O₂ → 12CO₂ + 14H₂O
α =2
β = 19
γ = 12
δ = 14
53.2moles of O₂
Step-by-step explanation:
Proper equation of the reaction:
αC₆H₁₄ + βO₂ → γCO₂ + δH₂O
This is a combustion reaction for a hydrocarbon. For the combustion of a hydrocarbon, the combustion equation is given below:
CₓHₙ + (x +
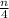 )O₂ → xCO₂ +
)O₂ → xCO₂ +
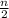 H₂O
H₂O
From the given combustion equation, x = 6 and n = 14
Therefore:
β = x +
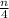 = 6 +
= 6 +
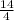 = 6 + 3.5 = 9
= 6 + 3.5 = 9
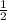
γ = 6
δ =
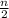 =
=
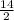 = 7
= 7
The complete reaction equation is therefore given as:
C₆H₁₄ + 9
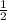 O₂ → 6CO₂ + 7H₂O
O₂ → 6CO₂ + 7H₂O
To express as whole number integers, we multiply the coefficients through by 2:
2C₆H₁₄ + 19O₂ → 12CO₂ + 14H₂O
Problem 2
From the reaction:
2 moles of hexane are required to completely react with 19 moles of O₂
∴ 5.6 moles of hexane would react with k moles of O₂
This gives: 5.6 x 19 = 2k
k =
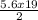
k = 53.2moles of O₂