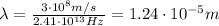Answer:
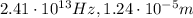
Step-by-step explanation:
The energy of the photon must be equal to 0.1 eV, so let's convert this value into Joules first:
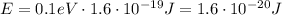
The energy of the photon is related to its frequency by
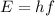
where h is the Planck constant and f is the frequency. Substituting,
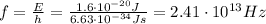
And now we can find the wavelength of the photon, which is given by
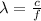
where c is the speed of light. Substituting,