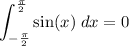Let F be the primitive of f, i.e.
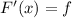
Then, we have
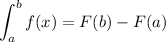
So, we have
![\displaystyle \int_0^5(2x-2)\;dx = \left[x^2-2x\right]_0^5 = 25-10=15](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/high-school/uwhheedeoahtg6dbuk7nu1v9adt92z9e1k.png)
As for the sine, we can spare the integral: the sine is an odd function, which means that it is symmetrical with respect to the origin. Any odd function integrated over a symmetrical neighborhood of zero (i.e. any interval of the form [-n,n]) returns zero: by symmetry, there is an equal amount of positive and negative area. So, we have