Answer:
A.) 4.0
Step-by-step explanation:
The general equilibrium expression looks like this:
![K = ([C]^(c) [D]^(d) )/([A]^(a) [B]^(b) )](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/3s4bgh0l8v4k9pgnpgqh.png)
In this expression,
-----> K = equilibrium constant
-----> uppercase letters = molarity
-----> lowercase letters = balanced equation coefficients
In this case, the molarity's do not need to be raised to any numbers because the coefficients in the balanced equation are all 1. You can find the constant by plugging the given molarities into the equation and simplifying.
![K = ([C]^(c) [D]^(d) )/([A]^(a) [B]^(b) )](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/3s4bgh0l8v4k9pgnpgqh.png) <----- Equilibrium expression
<----- Equilibrium expression
![K = ([2 M] [2 M])/([1 M] [1 M] )](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/ab7u2vh6t547t1vnr0mk.png) <----- Insert molarities
<----- Insert molarities
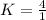 <----- Multiply
<----- Multiply
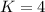 <----- Divide
<----- Divide