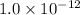Answer: The equilibrium constant for the above reaction is
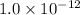
Step-by-step explanation:
Equilibrium constant in terms of concentration is defined as the ratio of concentration of products to the concentration of reactants each raised to the power their stoichiometric ratios. It is expressed as
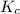
For a general chemical reaction:
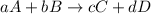
The expression for
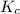 is written as:
is written as:
![K_(c)=([C]^c[D]^d)/([A]^a[B]^b)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/13aayk47tkvc79ferxww1rmrj9bfzrdqu4.png)
Concentration of solid and liquid substances in a chemical reaction is taken to be 1.
For the given chemical reaction:
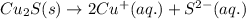
The expression for
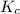 is written follows:
is written follows:
![K_c=[Cu^+]^2* [S^(2-)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/qd8wksc3ybg37r14l0yjtssfeo6fe4qk11.png)
We are given:
![[Cu^+]=1.0* 10^(-5)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/9y1a8i7awoyghm3az77q58495crq3iz2y6.png)
![[S^(2-)]=1.0* 10^(-2)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/y6kf23b9ka6jwq6m0r33l6ajq0rxnzy7rb.png)
Putting values in above expression, we get:
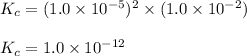
Hence, the equilibrium constant for the above reaction is